Cloud Security for Small Businesses: Ensuring Data Protection
Introduction
Cloud computing has become an essential tool for small businesses, offering flexibility, scalability, and cost savings. However, as businesses migrate to the cloud, they face a new set of cybersecurity challenges. From data breaches to insufficient backup plans, the risks associated with cloud adoption can be daunting. Fortunately, with the right strategies, small businesses can enjoy the benefits of the cloud while ensuring robust data protection.
In this blog, we’ll explore the benefits and risks of cloud adoption, the shared responsibility model, and essential cloud security measures, including guidance on choosing the right cloud provider. Drawing on lessons from the Aurora Case Study, we’ll highlight how proactive strategies can mitigate risks effectively.
Benefits and Risks of Cloud Adoption
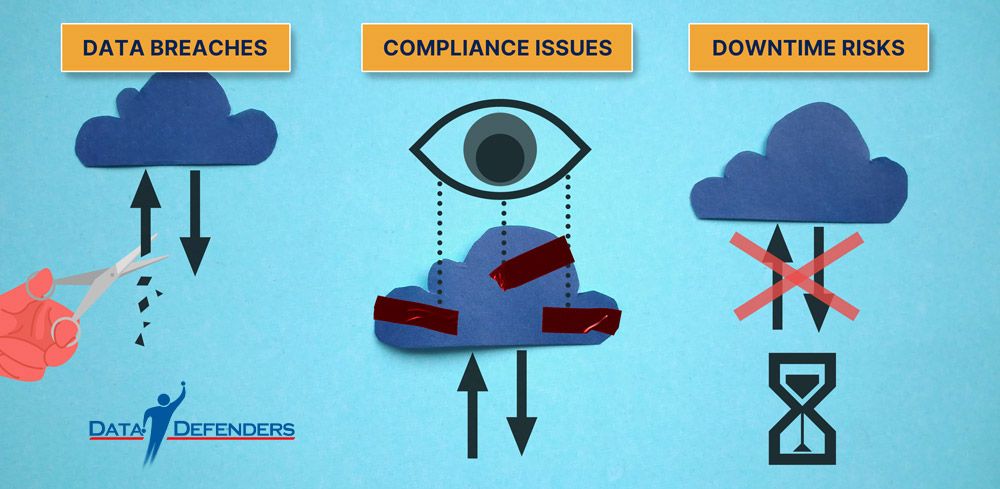
The cloud offers unparalleled advantages for small businesses: reduced IT costs, seamless remote work capabilities, and scalable resources. However, these benefits come with significant risks:
Data Breaches: Misconfigured cloud storage or unauthorized access can expose sensitive business data.
Compliance Issues: Businesses must adhere to regulations like GDPR, HIPAA, or federal/local mandates, which can be challenging in shared environments.
Downtime Risks: While cloud providers offer high uptime guarantees, outages can still disrupt operations if businesses lack proper contingency plans.
As highlighted in Week 4: Emerging Cybersecurity Threats for Enterprises, attackers are targeting cloud environments through supply chain vulnerabilities and phishing attacks.
Shared Responsibility Model
A common misconception among small businesses is that cloud providers bear all responsibility for security. The shared responsibility model clarifies that:
Cloud Providers are responsible for the security of the cloud (infrastructure, hardware, and physical data centers).
Businesses are responsible for the security in the cloud, including data, user access controls, and applications.
Understanding this distinction is critical to avoid gaps in security coverage. The Aurora Case Study illustrates how clear delineation of responsibilities helped the city maintain a secure environment while leveraging cloud solutions.
Key Cloud Security Measures
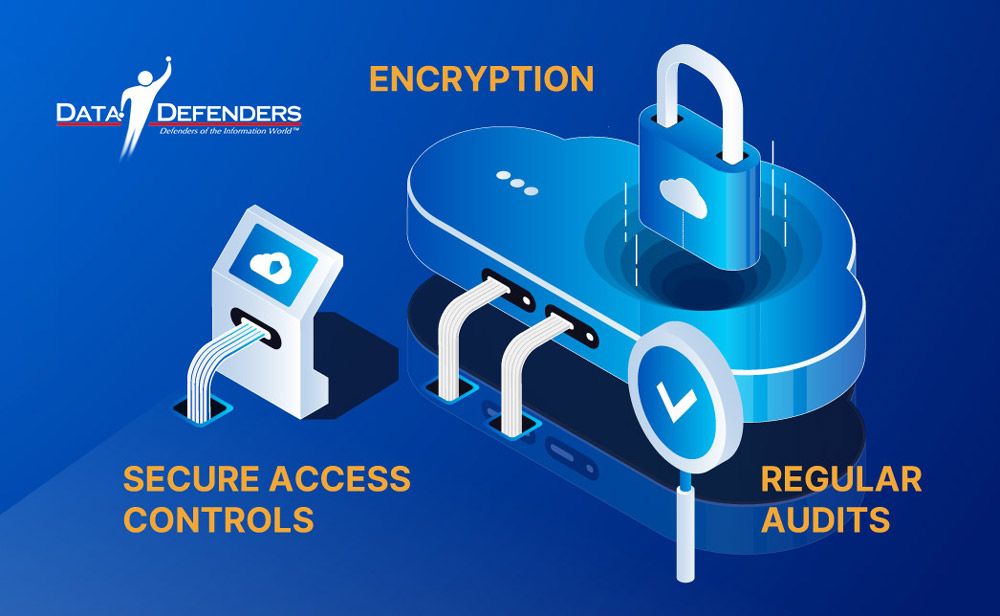
1. Encryption: Encrypting data at rest and in transit ensures that sensitive information remains protected, even if intercepted.
2. Secure Access Controls: Use multi-factor authentication (MFA) and role-based access control (RBAC) to restrict unauthorized access.
3. Regular Audits: Conduct routine security assessments to identify and address vulnerabilities in the cloud environment.
Drawing parallels to Week 2: Protecting Personal Data, robust encryption and secure access practices are foundational for safeguarding sensitive information.
Understanding this distinction is critical to avoid gaps in security coverage. The Aurora Case Study illustrates how clear delineation of responsibilities helped the city maintain a secure environment while leveraging cloud solutions.
Backup and Recovery Plans

An often-overlooked aspect of cloud security is the importance of automated backups and robust recovery strategies. Businesses should:
Automate Backups: Regular backups ensure that critical data is preserved and easily restorable.
Test Recovery Processes: Simulate scenarios to verify that backups can be quickly restored during outages or cyber incidents.
As discussed in Week 6: Cybersecurity Best Practices for Municipalities, proactive measures like these are key to maintaining operational continuity during cyberattacks.
Choosing the Right Cloud Provider
Selecting a cloud provider involves evaluating their security offerings and overall reliability. Key considerations include:
Security Certifications: Look for providers with certifications like ISO 27001 or SOC 2 compliance.
Uptime Guarantees: Providers should offer high availability with a minimum of 99.9% uptime.
Regulatory Compliance: Ensure the provider meets industry-specific regulations relevant to your business.
As seen in the Aurora Case Study, working with trusted partners like Data Defenders ensures alignment between technology and business needs.
Enhancing Cloud Security with MCOP

As small businesses navigate the complexities of cloud security, partnering with aManaged Cybersecurity Operations Provider (MCOP) like Data Defenders can make all the difference. MCOP provides ongoing threat detection, compliance management, and expert guidance to ensure cloud environments remain secure against evolving cyber threats.
Strengthen Your Cloud Security with MCOP
Cloud vulnerabilities can lead to devastating breaches—don’t leave your business at risk. Engage with our MCOP experts at Data Defenders for tailored cybersecurity solutions, real-time monitoring, and proactive defense strategies that keep your data secure.
Safeguard your cloud infrastructure, protect customer data, and ensure business continuity with MCOP.
Conclusion
While cloud computing offers significant benefits, small businesses must navigate its associated risks with care. By understanding the shared responsibility model, implementing key security measures, and choosing the right provider, organizations can secure their cloud environments effectively.
For more insights, exploreThe Rising Threat of Ransomware Attacksto understand how cloud vulnerabilities can lead to ransomware attacks, and Protecting Personal Data for strategies to safeguard sensitive information.
Ready to strengthen your cloud security? Contact our experts to learn more about tailored solutions like DataShield Cybersecurity 360°®. For real-world inspiration, check out the Aurora Case Study.

